NATS4 Logs Admin
Logs Admin
The Logs Admin lets you view information logged by NATS in an organized manner.
Before any information appears here, you must enable logging in the Configuration Admin. To do so, go to the NATS4 Configuration Admin and select "Logging" from the Current Section drop-down menu. Here, you will be able to enable logging for a variety of instances, including tracking, signup, e-mail, and cronjobs. After you have enabled logging for the instances you wish to keep a record of, go back to the Logs Admin.
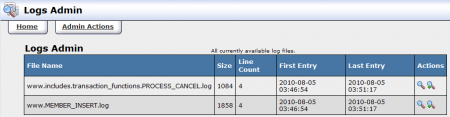
In the Logs Admin, you will find a list of logs that have been stored by NATS, as well as two action icons that correspond to each log. These icons are:
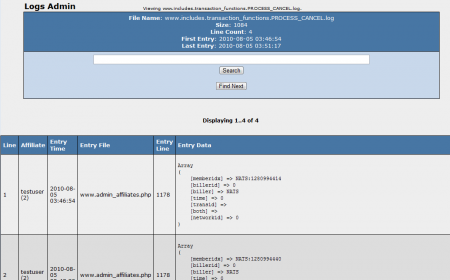
- View Log - Allows you to view a breakdown of each log in chronological order. This log display provides the line number, affiliate, entry file, entry line, and entry data of each specific log.
- Search Log - Allows you to search a selected log for specific information.
Admin Actions
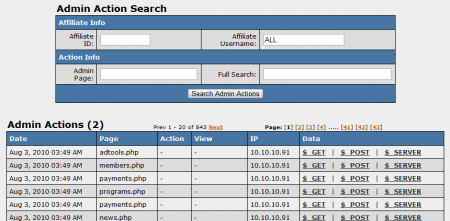
As of NATS version 4.0.74.1, we also offer an Admin Actions area in the Logs Admin. To access it, simply click the "Admin Actions" tab at the top of the page. This page allows you to keep track of actions taken by an admin, such as changing configurations. An advantage of this feature is that you (or a TMM tech) can troubleshoot problems by seeing what settings were changed, as well as when they were changed by an admin.
You can search for specific admin actions by using the "Admin Action Search" box at the top of the page. Available search parameters include:
- Affiliate Info: Search by Affiliate ID and Affiliate Username.
- Action Info: Search by Admin Page, or conduct a Full Search.
The breakdown of admin actions lists a variety of details, including:
- Date - The date an admin action took place.
- Page - What page the admin action took place on.
- Action - The action that the admin took (ex. customize_edit, edit_cascade, etc.)
- View - The specific sections of a page that the admin viewed.
- IP - The admin's login IP.
- Data - On mouse-over, shows a text bubble of information from $_GET, $_POST, and $_SERVER.